Hands off-Please Do Not Touch My Body, Yoga and Consent.
by Counseling and Wellness Center of PittsburghSeptember 30, 2018 counseling for anxiety, counseling for PTSD, psychotherapist, touch, yoga for trauma0 comments
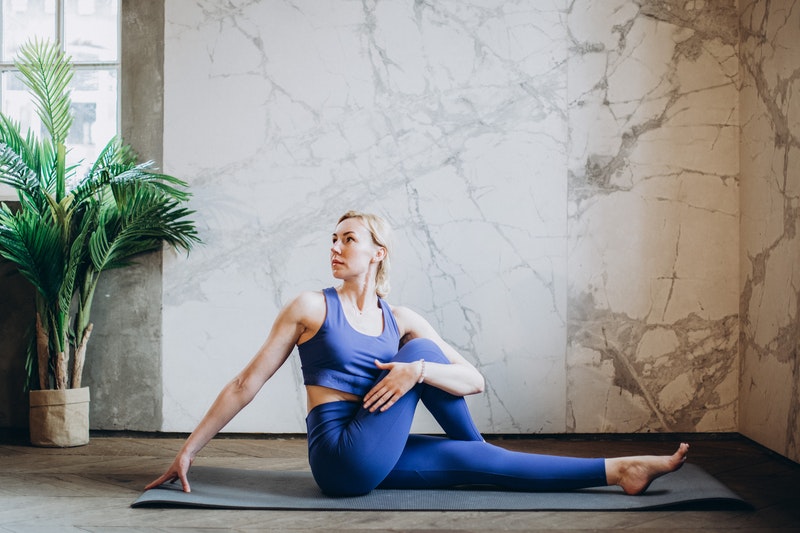
Consent, Please Do Not Touch My Body
Hands off-Please Do Not Touch My Body.
Closeness is sacred and powerful, and we should share it however we would like with a partner or partners with whom we have provided consent. Personally, I am a ‘toucher’, meaning I am a person who enjoys touch with my partner, someone who hugs family and friends and genuinely savors safe closeness. As we...Learn MoreTrauma Informed Care; We Have Evolved to be at risk for Trauma; Here is Why
by Counseling and Wellness Center of PittsburghJune 21, 2018 counseling for PTSD, psychology, psychotherapy, ptsd, trauma, trauma informed care, trauma therapy1 comment
Trauma Informed Care
We have fantastic and astonishing memory abilities, the human mind and its processes, particularly in the way we store and retrieve the effective memories which then effect the way that we store and respond to our other memories and sensory input. Evolutionary psychology examines the way some things that can be problematic are often helpful to us in the past and as we...Learn More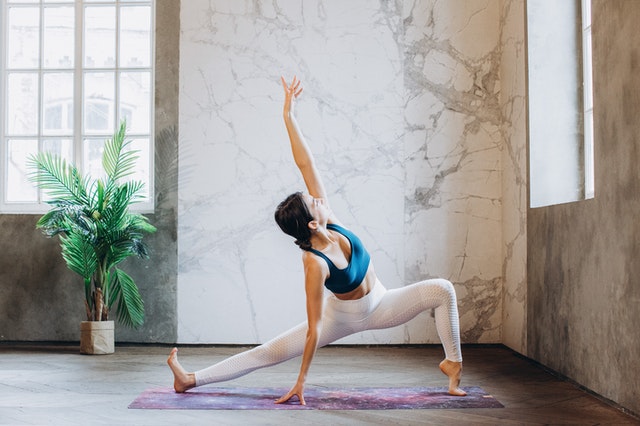
Yoga for Wellness
by Counseling and Wellness Center of PittsburghApril 14, 2018 counseling for depression, counseling for PTSD, meditation, mindfulness, nature therapy, Nutrition Counseling, outdoor yoga, stress managment, wellness counseling pittsburgh, wellness pittsburgh, yoga0 comments
Yoga. To many, the word conjures up images of Instagram perfection and beautiful backgrounds. Thousands of years ago, the poses (asanas) were only part of the defining point of a yoga practice. Yoga by ancient definition means “union.” A union of spiritual, emotional and physical practices of wellness. The poses are an integral part, but not comprehensive whole of the practice. Patanjali, one...Learn More